Michael Porter
- Environmental forces affect all of the Business Environment
- Porter five forces analysis - Wikipedia
- Porter's 5 Forces Definition
- Porter's Five Forces Explained with Examples | B2U
- Michael Porter's Five Forces model (to analyze competitive situations in an industry)
- Competitors
- price, advertising, customer service, merging firms, cutting costs, deals with clients, differentiation
- Competitors (= all existing firms, including our organization)
- Existing competitors (rivalries)
- increased competitive pressures: slow industry growth, high fixed costs
- Potential Entrants
- Entry
- Additional producers increase industry capacity and tend to lower prices
- Barriers to entry = business practices or conditions that make it difficult for new firms to enter the market = to deter new entrants in the market
- capital requirements, promotional expenditures, product identity, distribution access, switching costs
- Barriers to entry (into that industry)
- Suppliers
- Bargaining power of suppliers is great if few available substitute products
- Bargaining power of buyers and suppliers
- few buyers/suppliers, low switching costs
- Buyers
- Bargaining power of buyers is great if there are only a few buyers and many suppliers
- Bargaining power of buyers and suppliers
- few buyers/suppliers, low switching costs
- Substitutes
- Bargaining power of consumers is great if many available substitute products or if switching is facilitated (e.g. Internet shopping)
- Substitution possibilities
-
- Compare Porter's Five Forces model with the
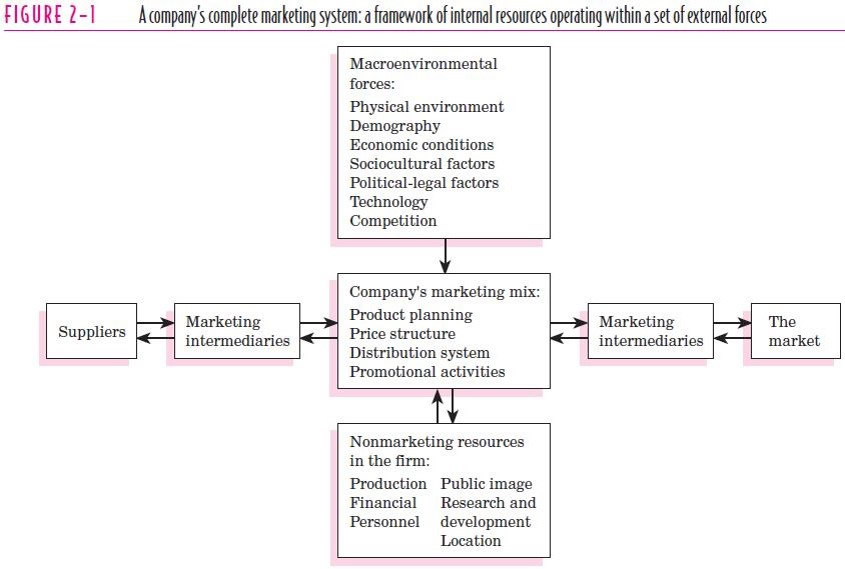
Marketing Micro-Environment
-
- Compare with the company's marketing system: